
Air Ng Windows Tutorial Drivers Of Your
SSE2 support is included to dramatically speed.Aircrack-ng is an 802.11 WEP and WPA-PSK keys cracking program that can recover keys once enough data packets have been captured. This Tutorial: Packets Supported for the PTW Attack page provides details. The content involved includes WEP encryption and WPA-PSK encrypted wireless network cracking operations.Aircrack-ng Windows Wpa Tutorial. Well, let me first explain that the content of this chapter is applicable to all mainstream brand wireless routers or APs on the market such as Linksys, Dlink, TPLink, BelKin, etc. Before you start to crack WPA/WPA2 networks using this Aircrack-ng tutorial, lets see a brief intro about it Airodump-ng with native wireless driver on Windows EDIT: This was an April Fool :) Altought this is not a final version (a work in progress), here is a version of airodump-ng that works on windows with the native drivers of your.
Air Ng Windows Tutorial Download BackTrack4 R2
For details, see Table 1 below for a specific list of components included in Aircrack-ng.Mainly used for WEP and WPA-PSK password recovery, as long as airodump-ng collects a sufficient number of data packets, aircrack-ng can automatically detect the data packets and determine whether they can be crackedUsed to change the working mode of the wireless network card so that other tools can be used smoothlyUsed to capture 802.11 data packets to facilitate aircrack-ng crackingDuring WEP and WPA-PSK password recovery, special wireless network data packets and traffic can be created as neededYou can connect the wireless network card to a specific port to prepare for flexible calls during attacksUsed in the WPA Rainbow Table attack to create specific database filesOther auxiliary tools, such as airdriver-ng, packetforge-ng, etc.Aircrack-ng has been built under BackTrack4 R2 ( download BackTrack4 R2 ), the specific calling method is shown in Figure 2 below: by sequentially selecting "Backtrack"-"Radio Network Analysis"-"80211"-"Cracking"-"Aircrack- ng "to open the main program interface of Aircrack-ng. Many of these tools will be used in the following content. To crack the password, run the aircrack-ng.Aircrack-ng (note the case) is a wireless attack audit suite that contains multiple tools. The tool is Using a wordlist attack.
We can see that there is no wireless network card except eth0.Make sure that the USB or PCMCIA wireless network card has been inserted correctly. First check which network cards are currently loaded, enter the command as follows: ifconfigAfter you press Enter, you can see the content shown in Figure 3 below. The specific steps for cracking WEP encryption with Aircrack-ng are as follows.In fact, many new people always have some doubts when they start to load the network card, so we will take a closer look at this basic operation. Aircrack-ng is the first choice among powerful weapons for cracking such encryption. Wireless networks that enable this type of encryption are often listed as one of the serious unsafe network environments.
This step is equivalent to enabling "Local Area Connection" under Windows. Explain that whether it is a wired or wireless network adapter, it needs to be activated, otherwise it will be unusable. Unlike the simple ifconfig command, you can see all the adapters connected to the current system network interface after adding the -a parameter.As shown in Figure 4 below, we can see that compared to Figure 3 above, there is a wireless network card named wlan0, which shows that the wireless network card has been recognized by BackTrack4 R2 Linux.Now that it has been identified, the wireless network card can be activated next.
This command is dedicated to viewing wireless network cards, not all adapters like ifconfig. As shown in Figure 5 below, at this point, the system has correctly identified the wireless network card.Of course, you can also view it by entering iwconfig. After loading, we can use ifconfig again to confirm. Here we will load the wireless network card that has been inserted into the notebook into the driver.
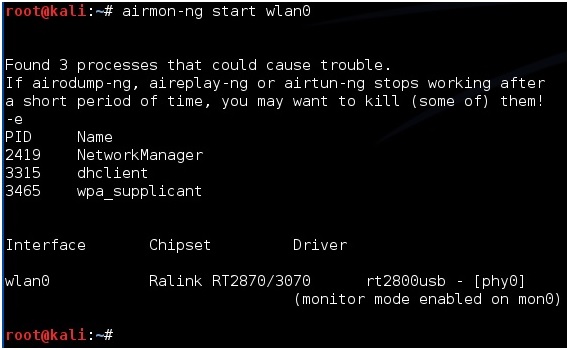
The default driver is rt73usb, which is displayed as "monitor mode enabled on mon0", that is, the monitoring mode has been activated. The Chipset chip type is marked as Ralink 2573 chip. The specific commands are as follows: airmon-ng start wlan0Start followed by the name of the wireless network card device, here refer to the name of the wireless network card shown in the previous ifconfig As shown in Figure 7 below, we can see the chip and driver type of the wireless network card. The same is true for wireless network sniffing.Under Linux, we use the airmon-ng tool in the Aircrack-ng package to implement it. Well, everyone knows that the network card used for sniffing must be in monitor monitoring mode. As shown in Figure 6 below.Step 2: Activate the wireless network card to monitor mode.For many Xiao Hei, various sniffer tools should be used to grab data messages such as passwords.
Just open a shell and enter the specific commands as follows: airodump-ng mon0Mon0 is the wireless network card that has been loaded and activated the monitoring mode before. The specific commands are as follows:However, before formal packet capture, pre-come detection is generally performed to obtain the current wireless network profile, including the AP's SSID, MAC address, working channel, wireless client MAC and number, etc. Here we use the airmon-ng tool in the Aircrack-ng package to implement it.
Be sure to pay attention to it. If you use the same file name longas to save, a file named longas-02.ivs will be generated. Well, the little black guys must pay attention to this: although we set the file name to be saved as longas here, the generated file is not longase.ivs, but longas-01.ivs.Note: This is because the tool airodump-ng is used to facilitate the later call of the crack, so the saved files are numbered in order, so there is a sequence number such as -01, and so on. Through the observation just now, the working channel of the wireless router that we want to conduct the attack test is 6 -w followed by the name of the file to be saved, where w is the meaning of "write", so enter the file name you want to keep, as shown in Figure 10 below, I will write here as longas. Here we directly target the AP whose SSID is "TP-LINK" and whose BSSID (MAC) is "00: 19: E0: EB: 33: 66 ”, the working channel is 6, and the MAC of the connected wireless client is“ 00: 1F: 38: C9: 71: 71 ”.Now that we see the target to be attacked in this test, that is the wireless router with SSID named TP-LINK, then enter the command as follows: airodump-ng -ivs -w longas -c 6 wlan0-ivs The setting here is to filter by setting, no longer save all wireless data, but only save IVS data packets that can be used for cracking, which can effectively reduce the size of the saved data packet -c Here we set the working channel of the target AP.
However, wireless hackers felt that such waiting was sometimes too long, so they used a method called "ARP Request" to read the ARP request message, and forged the message again to reissue it, in order to stimulate the AP to produce more Multiple data packets, thus speeding up the cracking process, this method is called ArpRequest injection attack. Cap when loading files The asterisk refers to all files with the same prefix.After you press Enter, you can see the interface shown in Figure 11 below, which indicates the start of wireless packet capture.Step 4: Use ArpRequest injection attack on the target APIf the wireless client connected to the wireless router / AP is interacting with large traffic, such as downloading large files using Thunder and eMule, the WEP password can be cracked by simply capturing packets. Of course they can, just use longas *.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
